Genetics
-
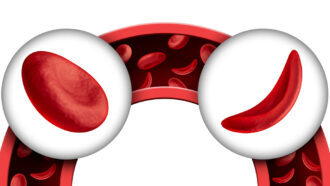 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExplainer: What is sickle cell disease?
Gene mutations can alter an individual’s hemoglobin in ways that curl their blood cells. This can cause painful sickle cell disease.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA in air can help ID unseen animals nearby
Analyzing these genetic residues in air offers a new way to study animals. It could give scientists a chance to monitor rare or hard to find animals.
By Laura Allen -
 Animals
AnimalsMeat-eating bees have something in common with vultures
Flesh-eating bees have acid-producing gut bacteria, much as vultures do. It lets them safely snack on rotting meat.
-
 Humans
HumansGenetics show humans likely trace back to Africa
Our history began looking ever more complex once geneticists revealed our ancestors picked up new DNA as they traveled across time and continents.
By Erin Wayman -
 Genetics
GeneticsExplainer: What is RNA?
A partner to DNA, cells use this molecule to translate the instructions for making all of the many proteins that your body needs to function.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWill the woolly mammoth return?
Scientists are using genetic engineering and cloning to try to bring back extinct species or save endangered ones. Here’s how and why.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCloning boosts endangered black-footed ferrets
A cloned ferret named Elizabeth Ann brings genetic diversity to a species that nearly went extinct in the 1980s.
-
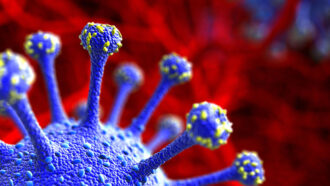 Microbes
MicrobesExplainer: Virus variants and strains
When viruses become more infectious or better able to survive the body’s immune system, they become a type of variant known as a strain.
By Janet Raloff -
 Plants
PlantsHow Romanesco cauliflower grows spiraling fractal cones
By tweaking just three genes in a common lab plant, scientists have mimicked one of nature’s most impressive mathematical patterns.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Genetics
GeneticsJust a tiny share of the DNA in us is unique to humans
Some of these tweaks to DNA, however, may have played a role in brain evolution.
-
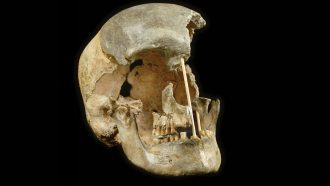 Genetics
GeneticsEurope’s ancient humans often hooked up with Neandertals
DNA from ancient bones shows humans and Neandertals were regularly mixing genes by about 45,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeThese rabbits can’t hop. A gene defect makes them do handstands
Mutations in a gene that helps nerve cells work properly rob rabbits of their ability to hop. Instead, the animals use their front paws to move.