Earth
Educators and Parents, Sign Up for The Cheat Sheet
Weekly updates to help you use Science News Explores in the learning environment
Thank you for signing up!
There was a problem signing you up.
-
 Earth
EarthAs Yellowstone’s supervolcano slumbers, another big danger lurks
Superheated water beneath Yellowstone could fuel hydrothermal explosions with the force of an atomic bomb. And lessons from the past suggest they could happen today.
By Douglas Fox -
 Tech
TechNew system uses evaporation to greatly cool artificial turf
It relies on rainwater that gets stored below a field of plastic "grass." The design also limits how much rain — and pollution — will run off artificial turf.
By Laura Allen -
 Space
SpaceHere’s why some shooting stars have long-lasting afterglows
Atmospheric chemistry is the most important factor in determining which meteors leave behind these persistent trails.
-
 Space
SpaceSummer ‘space hurricanes’ are emerging high above Earth’s magnetic poles
A separation — and later recombining — of Earth’s magnetic field lines may be what churns up these super-high-altitude storms of plasma.
-
 Climate
ClimateStashing more CO2 in the ocean could slow climate change
More research is needed on ways to safely remove some CO2 from the water to make room for more — such as by seaweed farming and iron fertilization.
-
 Earth
EarthSuperman’s kryptonite doesn’t have a true equal on Earth
Though not quite kryptonite, some Earth minerals can glow under ultraviolet light. Excited electrons cause these real-life power stones to light up.
-
 Tech
TechLasers help put the cork on spilled oil
Treating cork with lasers made the material able to quickly sponge up oil while repelling water, scientists in China and Israel found.
-
 Earth
EarthHawaii’s Kilauea volcano recently erupted like a stomp rocket
This appears to be a newfound type of eruption. It could only be recognized because of the extensive monitoring of Kilauea's crater.
-
 Climate
ClimateMicrobes in the Arctic may be releasing more climate-warming gases
Mini greenhouses in the wild show how the tiny organisms lurking underground in a ‘sleepy biome’ could play a big role in climate change.
-
 Earth
EarthAnalyze This: Where are U.S. earthquakes most likely?
A model used data on historical quakes and measurements from active faults to forecast risks of damaging earthquakes in the next 100 years.
-
 Animals
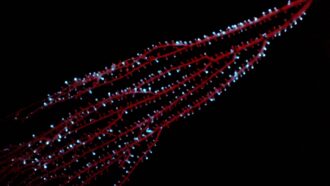
AnimalsCorals may have been the first life forms to glow in the dark
Ancestors of modern octocorals may have lit up the deep sea as far back as 540 million years ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Climate
ClimateClimate change is changing how scientists measure time
Polar ice sheets are melting faster. This is slowing Earth’s spin, which changes how we sync our clocks to tell time.